What is an LPG Gas Bottle and what are the different types?
This article is a guide for LPG gas bottles, what they are used for, how they work and how to use them safely.
The following related tutorials complement this article:
LPG installation in a recreational vehicle like a RV Camper, Caravan or Food Truck
LPG Vapor Tanks for RV Campers, Caravans and Food Trucks
Pressure Regulators for Gas Bottles and Vapor Tanks
Installation instructions for LPG cylinder tanks (vapor tanks) in (recreational) vehicles
The EN 1949 Standard: The European Standard for Safe LPG Systems in RVs and Caravans
LPG Gas Bottles
This component is responsible for storing the liquid LPG and also vaporizing it, so that the gas leaves the gas bottle in gaseous form. LPG gas bottles (also called LPG gas cylinders) come in different sizes and can be made from different materials such as steel, aluminum, or plastic (composite). The LPG gas bottle must be equipped with a valid approval depending on the type of LPG gas bottle and the type of use.
An LPG gas bottle stands upright (vertical position) and is equipped with a base with a foot on which it can be placed. The tank valves on an LPG gas bottle are located at the top.
LPG Gas Bottles must be approved according to one of the following guidelines, depending on the type of use.
2010/35/EU Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive (TPED): This directive regulates the road, rail, and water transport of transportable pressure equipment within the EU. It therefore concerns equipment that is under pressure and is transported, such as LPG gas bottles. The purpose of this directive is to ensure safety during the transport of these dangerous goods. It sets requirements for the design, manufacture, and inspection of this equipment (Gas bottle), so that it can be safely transported by road, rail, or water.
2014/68/EU Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) regulates the safety of pressure equipment (LPG gas bottle) when it is in operation.
Overlap in requirements for 2010/35/EU and 2014/68/EU: There is a large overlap between these first two directives. The essential safety requirements for a gas bottle (strength, material, design) are largely the same for both transport and use. Manufacturers will therefore often have a combined assessment carried out so that their product complies with both directives.
ECE Regulation No. 67 This is a strict and very safe ECE directive for the approval of LPG components for automotive applications, such as an LPG tank (LPG gas bottle tank) and its use in a vehicle.
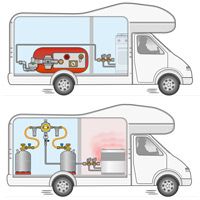
LPG Gas Storage in an LPG Gas Bottle. How does it work?
The most important component of the LPG system is the LPG gas bottle (or several) (or LPG tank) for storing the LPG. The choice between a gas bottle or a gas tank depends on the required storage capacity and the available space in or under the RV, caravan, or food truck.
An LPG gas bottle is filled and stored with liquid LPG, but a small amount also vaporizes and collects in the upper space of the LPG gas bottle. The gas is withdrawn from the upper space, so that the gas leaves the LPG gas bottle in gaseous form and the pressure in the LPG gas bottle drops. Due to the pressure drop, liquid LPG vaporizes again, causing the pressure to rise again. The vaporization of the LPG requires heat (energy). When the LPG vaporizes, the gas bottle therefore cools down slightly. The more heat is available, the easier the LPG vaporizes and the pressure increases. With high gas consumption, a lot of LPG will also vaporize, causing the LPG gas bottle to cool down significantly. The vaporization process will therefore become increasingly difficult.
Vaporization Process and Temperature Dependence
The vaporization process requires heat extraction from the environment. Propane vaporizes better at low temperatures than butane. As a result:
- The gas pressure in the gas bottle is highly temperature dependent
- Pressure can drop during high consumption and cold conditions
- Consider an additional (external) gas bottle for more vaporization capacity in case of high demand
Examples of LPG gas bottles
The Most Important General Safety Regulations for LPG Gas Bottles
- Always keep the gas bottle upright. (with the valve at the top)
- Do not drop the gas bottle, as damage can occur to the bottle or the couplings.
- Do not store the gas bottle near an open flame.
- Do not use or store below ground level. Leaked gas will accumulate at a low level.
- The storage space must be well ventilated with the outside.
- Do not use tools to open the valve.
- Always use a pressure regulator to reduce the gas pressure from the gas bottle and regulate it to the correct working pressure.
- Gas bottles and pressure regulators are equipped with an overpressure valve, for this reason these parts must not be placed indoors. They should be in a ventilated space, which is connected to the outside air and not connected to the interior.
- Check the hoses regularly and see if the cylinder is securely fastened. If the hoses are damaged or show signs of wear, replace the hoses (use hoses of the correct quality).
- Handle and respect the applicable European and national guidelines.
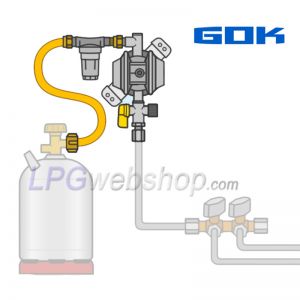
Always use a pressure regulator! Why is it needed?
A pressure regulator is connected (with or without the use of a high-pressure gas filter and/or high-pressure hose) to the outlet of an LPG gas bottle, with the aim of reducing and regulating the pressure to a low, stable, and safe working pressure, in most cases 30 mbar. This pressure reduction is necessary because the pressure coming from the LPG gas bottle is many times too high. The pressure in an LPG gas bottle varies, depending on temperature, between 1 and 20 bar. This pressure is WAY too high for the gas appliances. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the pressure to a constant, safe and low pressure.
To learn more about types of pressure regulators, safety requirements and installation instructions, we refer to the article: Pressure Regulators for Gas Bottles and Vapor Tanks
Examples of pressure regulators
Types of connections on the extraction valve on an LPG gas bottle.
Unfortunately, there are many different types of connections on LPG gas bottles. Depending on the country of application, one type or another is used. But in most European countries, a variant of the SHELL connection with W21.8 Left-hand thread is used. The difference usually lies in the type of seal and central fit.
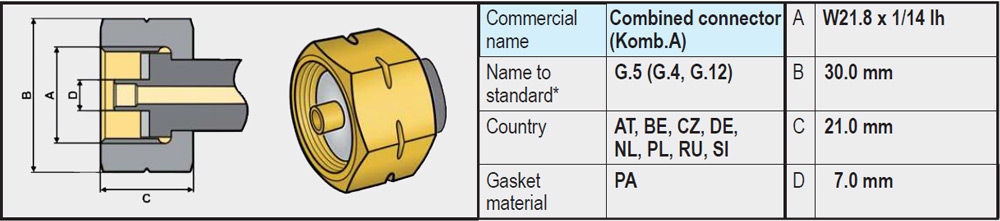
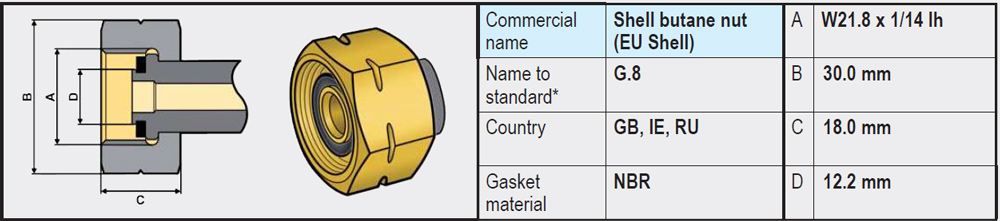
- Types G.2 / G.4 / G.5 / G.8 (W21.8 x 1/14 left-hand thread): These variants are very similar and on the gas bottle side have no rubber seal and are completely made of brass. The sealing is on the side of the regulator or high-pressure gas hose, often in the form of a rubber or plastic ring.
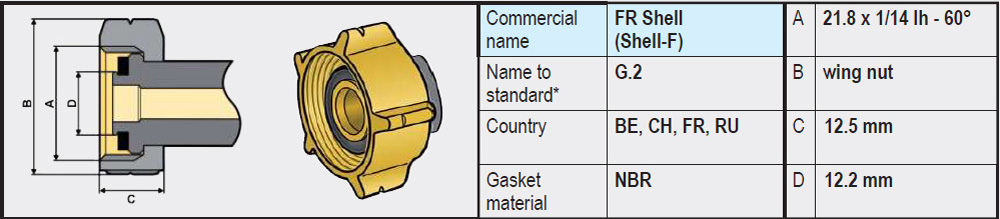
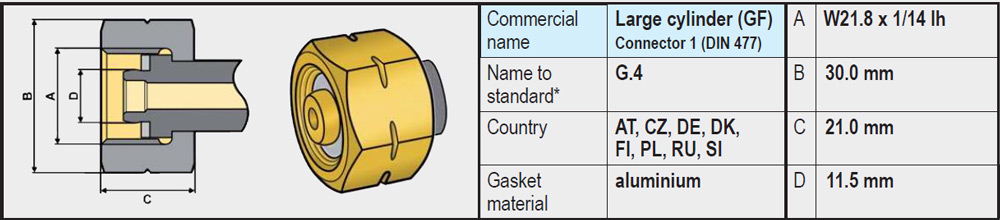
- Type G.12 (W21.8 x 1/14 left-hand thread): Differs slightly from the connections mentioned above and on the gas bottle side does have a recessed rubber sealing ring. The coupling of the regulator has an integrated annular brass rim that is pressed into the rubber ring on the gas bottle side when tightened and provides a seal.
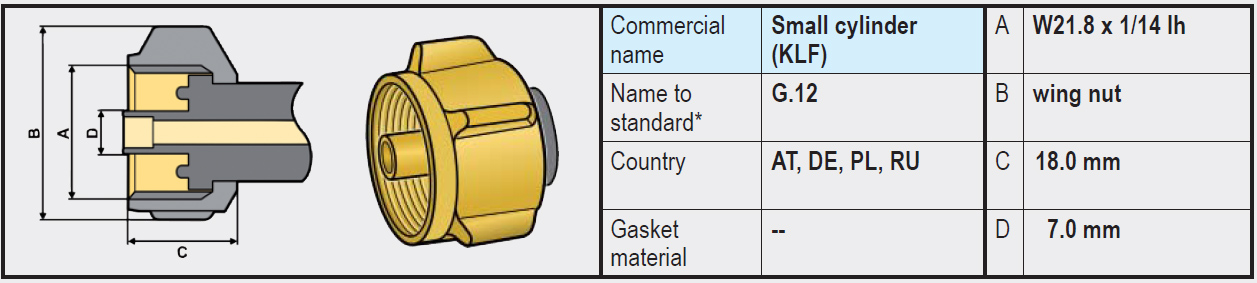
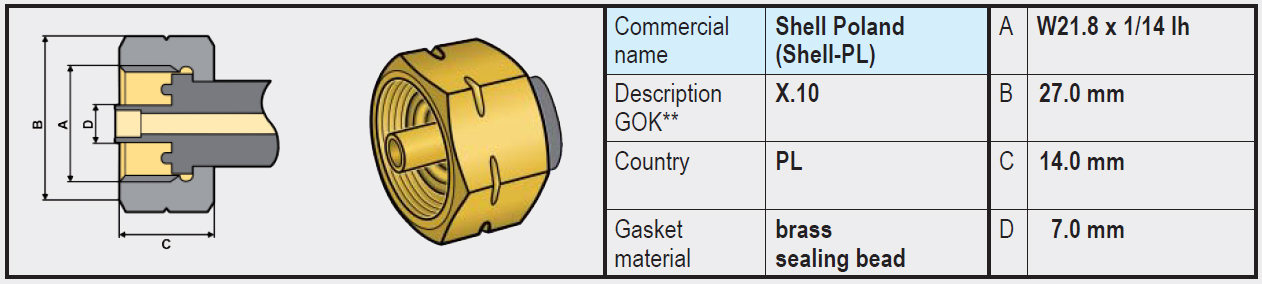
Note: It is not possible to connect a regulator (or high-pressure gas hose) with a G.12 coupling (with integrated annular brass rim) directly to an LPG gas bottle with type G.2 / G.4 /G.5 / G.8 (without rubber); a seal will not be created (brass on brass). In that case, use an adapter (G.5 to G.12) that we offer in our webshop.
A regulator (or high-pressure gas hose) with a G.5 coupling, on the other hand, will fit on a gas bottle with a G.12 connection. The G.5 connection is therefore also called a Kombi coupling, because it fits both on a G.2, G.4, G.8 and on a G.12.
Exceptions are:
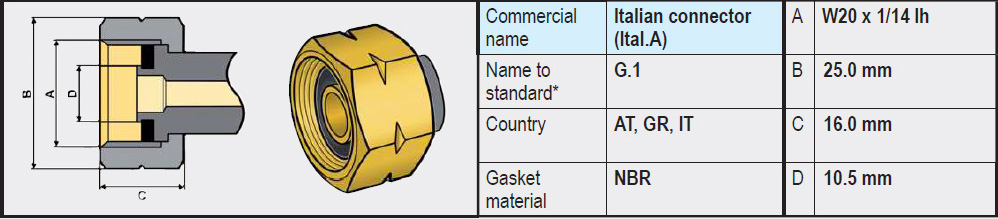
In Italy, Greece, Austria, Slovenia, the G.1 connection is often used, which uses left-hand W20 thread instead of left-hand W21.8 thread. It therefore looks very much like a SHELL connection, but is slightly smaller. In our webshop, we also offer adapters that make it possible to reduce an LPG gas bottle with the slightly larger W21.8 thread to W20, so that it can be used in an Italian RV camper and connected to a G.1 regulator (or high-pressure gas hose).
- Type G.1 (W20x1/14 Left-Hand Thread) Widely used in the countries (Italy, Greece, Austria, Slovenia). Has no rubber seal on the gas bottle side and is completely made of brass. The sealing is on the side of the regulator or high-pressure gas hose, often in the form of a rubber or plastic ring.
In addition, there are connections of the POL and Clip-on type, but since they are not often used in European countries, we will not consider them further.
Examples of Adapters for Gas Bottles
We distinguish between exchangeable LPG gas bottles and refillable LPG gas bottles.
Refillable LPG Gas Bottle:
A refillable LPG gas bottle (also called an LPG gas bottle tank) must at least be equipped with a number of safety features such as an 80% fill limiter, an overpressure valve, a flow limiter, and a closable extraction valve (Manual or Electric), and a valid approval/certification.
The mentioned safety features come in different versions such as:
- with a separate 80% fill valve and a separate manual extraction valve with integrated overpressure valve (like on the RV gas bottle),
- one with everything integrated into a single manual valve (Overfill Protection Device)
- a MultiValve with integrated separate 80% fill valve connection, separate extraction valve with connection and overpressure valve.
The advantage of an LPG gas bottle with connections and valves like type A and C (so with separate connections for the inlet and outlet) is that the filling hose can be connected to the inlet and a pressure regulator or high-pressure gas hose can remain connected to the outlet. So that when refueling, the filling hose does not have to be swapped with the high-pressure hose.
OPD Gas Bottles are LPG Gas Bottles equipped with a component called an Overfill Protection Device, which means that these gas bottles are equipped with an 80% fill limiter, an overpressure valve, and a manual extraction valve with flow limiter, all integrated into this one component. These safety features make an OPD gas bottle much safer than a regular exchangeable LPG gas bottle. However, the disadvantage of this type of gas bottle is that both filling with LPG and gas extraction take place via one and the same inlet/outlet. Because there is only one connection on an OPD gas bottle. Therefore, the use of an OPD gas bottle (type B) is highly discouraged for internal use in an RV camper, caravan, or food truck. An OPD gas bottle (type B) may be more suitable as an external LPG gas bottle. Via a high-pressure quick coupling, it can be connected to the LPG system. First study the regulations carefully to determine if this is possible for your RV camper or caravan.
The connection (inlet and outlet) on an OPD gas bottle is in most cases of the SHELL connection type G.12 = W21.8 x 1/14 (M22) with left-hand thread and with a rubber sealing ring.
Multivalve Gas Bottles, like OPD gas bottles, are equipped with a unit with safety features such as an 80% fill limiter, an overpressure valve, and a manual extraction valve with flow limiter, all integrated into a MultiValve, but with the big difference that the inlet (for filling) and the outlet (for gas extraction) are separate. This means that, technically, the pressure regulator (or high-pressure gas hose) can remain connected to the outlet of this type of LPG gas bottle during filling. Also, a Multivalve is equipped with a non-return valve in the filling connection, which prevents gas from escaping back from the gas bottle via the inlet, while an OPD gas bottle does not have this.
- The inlet (filling side) of a MultiValve gas bottle is usually a 1/2" UNF Flare connection (suitable for LPG filling hose)
- The outlet (gas extraction) of a MultiValve gas bottle is usually of the SHELL connection type G.12 = W21.8 x 1/14 (M22) with left-hand thread and with a rubber sealing ring. (Just like an OPD gas bottle)
Examples of LPG gas bottles
Exchangeable Gas Bottles:
An exchangeable LPG gas bottle is not being filled while it is in a vehicle and is instead exchanged when it is empty. For this reason, an exchangeable LPG gas bottle does not necessarily have to meet the (previously mentioned) requirements for refillable LPG gas bottles. A refillable LPG gas bottle can, however, be used as an exchangeable LPG gas bottle.
The filling of an exchangeable LPG gas bottle is therefore done outside the vehicle (by an authorized LPG gas bottle filling station). An exchangeable LPG gas bottle can also be a refillable LPG gas bottle, as described above, but may not be refueled in a vehicle, because, for example, it does not have the correct approval, or the entire installation has not been certified or does not meet the installation requirements.
An exchangeable LPG gas bottle must be securely fastened in the vehicle, but must also be removable without tools.
The use of LPG Gas Bottles in recreational vehicles such as RV campers and caravans.
If you decide to use a (refillable) LPG gas bottle in your RV camper (also called Motorhome), caravan, or food truck, then this LPG gas bottle must meet the safety requirements mentioned earlier and be equipped with a valid approval/certification. But also the fastening of the LPG gas bottle and the entire LPG installation must meet the correct safety requirements, installation instructions, and certifications. (in the paragraphs below, we write more about this).
These are the most important safety regulations regarding LPG gas bottles in recreational vehicles.
- Have the installation of the gas bottle(s) done by a recognized and authorized specialist.
- Have the LPG system certified.
- Always keep the gas bottle upright (with the valve at the top) so that only gas in gaseous form leaves the gas bottle.
- Do not drop the gas bottle, as damage can occur to the bottle or the couplings.
- The storage space / compartment must be well and sufficiently ventilated with the outside and furthermore meet the requirements in EN 1949.
- Observe the minimum distances to a heat source such as an exhaust, as mentioned in EN 1949.
- Furthermore, observe the safety requirements as mentioned in EN 1949 and ECE Regulation 122 annex 8.
Note when using 2 gas tanks (or gas bottles)! :
When using 2 LPG gas bottles or 2 LPG vapor tanks, the outlets of the gas tanks must not be directly connected to each other. It must be technically impossible for gas to flow from gas tank A to gas tank B. For this, a changeover device is used that ensures the gas bottles are never interconnected and automatically prevents gas from escaping if 1 of the 2 gas bottles is not connected. Pressure regulators intended for the use of 2 gas bottles are usually equipped with such a changeover device.
Note when using an EXTERNAL gas bottle or gas tank! :
- Vehicles with a gas bottle compartment with internal access may not use an external gas supply (gas bottle or gas tank).
- When using a quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) to connect an external gas supply (gas bottle or gas tank) in addition to the use of an internal existing gas source (gas bottle or gas tank), it will be permanently fixed and a changeover device, as mentioned above, will be applied.
- Such a quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) will be installed in the gas bottle / gas tank compartment or externally on the wall of the compartment.
- If this quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) is installed in the gas bottle / gas tank compartment, it will be possible to connect an external gas supply and then close the compartment again, without causing any damage to the supply gas hose.
- The supply pressure from the external gas source must not be lower than 0.3 bar and not higher than 2.2 bar. The quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) will be provided with a permanently attached label or sticker indicating this minimum and maximum inlet pressure. For the use of an automatic changeover device, a minimum pressure of 1.0 bar is recommended.
- The quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) will be incompatible with any low-pressure quick coupling (gas extraction quick-connect coupling).
- The quick-connect coupling (high-pressure quick coupling) will be protected against dirt and water by the use of a cap.
If you want to learn more about LPG installations in recreational vehicles such as RV campers and caravans and the associated safety requirements and installation instructions, then we recommend the following article: LPG installation in a recreational vehicle like a RV Camper, Caravan or Food Truck
Ensure a proper fastening of the LPG gas bottle.
An LPG gas bottle in a vehicle such as an RV camper (also called Motorhome) and Food Truck must of course be securely fastened so that it cannot come loose and move while driving or in the event of a collision. So make sure it is attached to the vehicle with a sturdy construction. The EN 1949 guideline and the G 607 regulations indicate how an exchangeable LPG gas bottle should be fastened in a vehicle. Refillable LPG gas bottles that are refueled while they are in the recreational vehicle must be permanently fastened and connected in the vehicle according to the installation requirements in EN 12979 (or the applicable national guidelines such as the RDW LPG installation methods in the NL). The exact method of fastening depends on the size of the gas bottle and the positioning.
Here we mention a few basic regulations:
- LPG Gas Bottles must be securely fastened in the vehicle so that they remain in their position while driving or in an accident.
- The method of fastening an LPG gas bottle depends on whether it is used as an exchangeable or a refillable LPG gas bottle. For exchangeable LPG gas bottles, it is required that their fastening must be openable without tools. Whereas for refillable LPG gas bottles, they must be permanently fastened and connected.
- Always place an LPG gas bottle upright. (with the valve at the top), so that the valves on the tank function correctly and only gas in gaseous form leaves the gas bottle.
- See further the safety requirements and regulations mentioned earlier in this article.
Examples of fasteners for gas bottles
LPG Refueling. May I fill my LPG installation at a regular LPG pump station with LPG?
To be allowed to fill an LPG tank or refillable LPG gas bottle with LPG while it is positioned in the recreational vehicle, it and the entire installation must meet various applicable safety requirements and be equipped with the correct approval. In some cases (countries), it is necessary to demonstrate that the entire gas system has been approved. (via G 607 approval stickers or registration on the vehicle registration documents).
In addition to the safety requirements mentioned earlier, we list below a number of additional safety requirements regarding LPG refueling:
- The electrically or manually operated extraction valve directly on the outlet of the gas tank / LPG gas bottle must always be closed during LPG refueling. If a manual extraction valve is used, it must be located and operable in the immediate vicinity of the LPG filling connection on the vehicle. Otherwise, an additional manual valve will be placed upstream of the pressure regulator that is located and operable in the immediate vicinity of the LPG filling connection on the vehicle, or an additional automatic valve will be placed upstream of the pressure regulator.
- The operation of an electric extraction valve must be directly and easily accessible.
- A refillable LPG gas bottle / LPG tank must be equipped with a number of safety features such as an 80% fill limiter with non-return valve, an overpressure valve, a flow limiter, and a closable extraction valve (Manual or Electric) and a valid approval (UN/ECE Regulation No. 67).
- A refillable LPG gas bottle / LPG tank must be permanently and sufficiently securely fastened in the vehicle (According to EN 12979 or the applicable national guidelines)
- The installation from the filling connection up to and including the gas tank must meet the safety requirements mentioned in EN 12979 (or the applicable national guidelines such as the RDW LPG installation methods in the NL).
- The installation from the filling connection to the gas tank and from the gas tank to the pressure regulator must undergo a leak test using a leak detection fluid.
- The entire LPG installation must meet the safety requirements (EN 1949 / G 607 / EN 12979), be equipped with a valid approval, and in some countries also be registered on the vehicle registration.
Furthermore, there may be additional conditions or prohibitions per country and pump station. For example, self-refueling LPG or filling gas bottles is not permitted in every country.
ATTENTION! Note that in some countries (Italy and a number of Eastern European countries) self-refueling LPG is not allowed. This may only be done by the personnel of the gas station. Inform yourself about the rules of each country where you intend to refuel.
TIP! When filling the LPG tank or LPG gas bottle for the first time
In addition to a mandatory leak test, it is advisable to check the gas tank and connections (such as the valves on the tank, the filling hose, and filling connection) extra carefully for any leaks before filling the gas tank with LPG. To pressurize the gas tank, you can simply connect the refueling nozzle from the LPG pump station to your filling connection (without activating the pump). This causes a limited amount of LPG from the refueling nozzle and hose to flow into the gas tank, as it is still pressure-free. This limited amount of LPG vaporizes in the gas tank and thereby builds up a gas pressure in the gas tank that is sufficient to detect any leaks. LPG also has a strong odor, so a leak should also be noticeable because of that. Check carefully for leaks with a gas leak detection spray (or as an alternative a plant sprayer with soapy water) and spray it on the various couplings and connections. Only when you know that everything is leak-free and properly connected is it possible to fill the tank further.
Product examples of LPG filling parts
This article is protected by copyright. (Partially) copying this article is prohibited.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is intended solely as an aid and has been compiled to align as well as possible with applicable regulations and guidelines. National regulations may differ or impose additional requirements. Installers and users are themselves responsible for (having) the gas installation checked and complying with applicable local laws and regulations. Always consult a certified professional for this.
Despite the care with which this information has been compiled, there is the possibility of errors and omissions. No rights can be derived from this article. The most recent and local official standards and regulations are always leading.
In addition to this specific disclaimer, our general disclaimer also applies, the link to which can be found in the menu in the footer (page end).